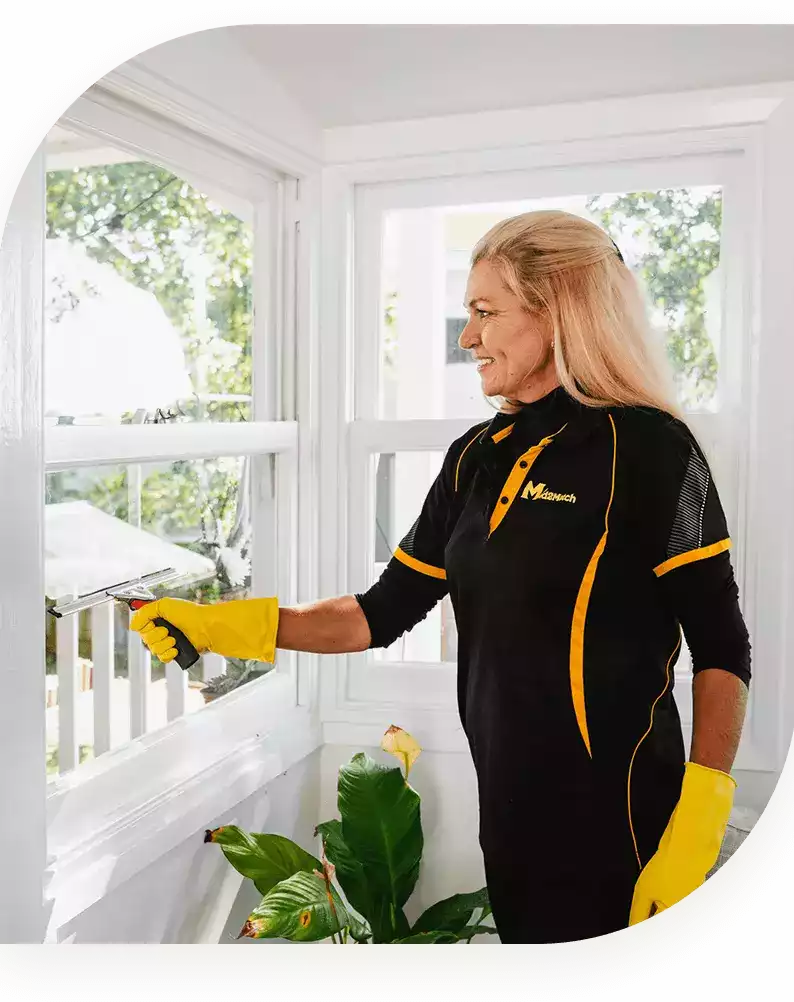
Get The Best House Cleaning In Winthrop

Professional, vetted cleaners

Friendly customer support

Recurring discounts

WHY MAID2MATCH?
More Than Just A Cleaning Service

Easily book & pay online
Appointments are booked online with one simple process, using your phone or computer.

The same cleaners every time
A team that you can trust to do the best job each time, every time.

Cleaning equipment provided
For your convenience, our team brings their own cleaning equipment for each service.

Adaptable to your needs & preferences
We work to be flexible and adapt our services to your cleaning needs.

Convenient booking management
Whatever you need regarding your service, we’re just a message away!

No lock in contracts for ongoing services
You control your services, with no locked-in long-term contract.
1800 207 686
MAKING YOUR HOME SPARKLE
Winthrop House Cleaning Services

Hourly Rate Cleaning
Choose this for: you need a quick cleaning job, or a tidy-up in specific areas. This time-based service means our cleaners will accommodate your cleaning priorities or focus on what needs cleaning the most. They’ll also only work to the allotted time.




Flat Rate Cleaning
Choose this for: you need a full, thorough clean or a specific set of services. This fixed price service means our cleaners will follow our detailed service checklist, and only stop when every task is done. Extras are available at additional flat rates.
What's Included in The Flat Rate?
 Vacuuming & Mopping
Vacuuming & Mopping Sweeping & Dusting
Sweeping & Dusting Cleaning The Bedrooms
Cleaning The Bedrooms Cleaning The Bathrooms
Cleaning The Bathrooms Cleaning The Toilets
Cleaning The Toilets Cleaning The Kitchen
Cleaning The Kitchen Cleaning The Sinks
Cleaning The Sinks Cleaning The Stovetop
Cleaning The Stovetop Cleaning The Living Spaces
Cleaning The Living Spaces

Deep Cleaning
Whether you’re preparing for guests or you want a more thorough spring clean of your home, Maid2Match is ready to deliver. We’ll have every nook, cranny, and corner spotless. From mopping floors, to scrubbing toilets and tubs, our team will have your home sparkling from top to bottom.
Flat Rate Cleaning Extras
| Deep clean | $90 |
| Clean interior windows | $60 |
| Additional room/s | $28 |
| Oven clean | $40 |
| Housekeeping | $20 |
| One load of laundry | $20 |
| Clean inside the fridge | $20 |
| Clean inside cabinets | $20 |


100% Satisfaction Guarantee
We are confident that our cleaning service will exceed your expectations. However, if you are not 100% satisfied with our services, please get in touch with us and we’ll send a team to set things right. If you’re still not happy, we’ll offer a refund on your booking.
OUR TEAM
We Have Local Cleaners In Winthrop
Lorena
Maid2Match Professional
Brigitte
Maid2Match Professional

Nikita
Maid2Match Professional
Your home is safely insured with us

4.3/5 stars on Trustpilot 200+ Reviews • excellent

150+ FIVE STAR REVIEWS ON GOOGLE
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Winthrop Cleaning Information
What time are your services available?
You can enlist your service anytime between 8:00am and 5:00pm, Monday to Saturday. We allot a 30 minute window for when the service will commence, so you know exactly when to expect our cleaner’s arrival.
What services are included?
We offer hourly rate cleaning for specific home areas and quick tidy-ups, or flat rate cleaning for more comprehensive cleaning jobs and additional tasks. Each booking is different and will depend on your cleaning requirements and preferences. You can book specific services only, or opt for a deep clean that follows our detailed checklist.
How much does it cost to clean my house?
We have two pricing alternatives: flat rate and hourly rate. Choose which option best suits your cleaning needs, then use our easy online form for a prompt quote!
Are cleaning supplies provided?
The cleaning team from Maid2Match brings their own (eco-friendly) supplies and tools for your convenience. If you’d prefer we use any particular cleaning agents, feel free to inform us and we’ll use any products you leave out.
Are your cleaning supplies safe for children and pets?
We only use products that are eco-friendly and safe for use around both young children and pets.

How does a recurring service work?
You can indicate your desired cleaning frequency on our booking page! We offer significant discounts depending on how regularly you want us to tidy up your house. We also don’t lock you into long-term contracts, so you have complete control over your cleaning schedule.
How easily can I book online?
It only takes a minute. Simply fill out our booking form, then pay through our secure payment process to finalise your service.
What forms of payment do you accept?
We only accept payment via credit or debit cards. You won't need to worry about having cash on the day of your cleaning job. The site processes online payments via Stripe, and uses safe security protocols to protect your information.
Do I have to be home for the cleaning service?
Nope! Just leave the key for entry and our cleaning team will take it from there. Inform our team how they’ll access your house, then rest assured that our team will do a thorough job while maintaining the safety and security of your home.
How long does it take to clean my house?
If you opt for the hourly rate option, our cleaning team will only work in the time you allot to them. For fixed rate cleaning, the size of your home and the selected services will determine the time. Our team will discuss this with you ahead of your service.
LOCAL HOUSE CLEANERS
Other Locations We Clean Near You
Perth Suburbs
- Applecross
- Attadale
- Balcatta
- Bayswater
- Bicton
- Canning Vale
- Carine
- City Beach
- Claremont
- Como
- Cottesloe
- Dianella
- Duncraig
- East Victoria Park
- Floreat
- Fremantle
- Greenwood
- Hamilton Hill
- Hillarys
- Joondalup
- Kardinya
- Karrinyup
- Kingsley
- Leeming
- Maylands
- Morley
- Mosman Park
- Mount Lawley
- Mount Pleasant
- Nedlands
- Ocean Reef
- Palmyra
- Scarborough
- Sorrento
- Spearwood
- Subiaco
- Wembley
- Wembley Downs
- Willetton
- Winthrop
- Woodvale
- Yokine
 Vacuuming & Mopping
Vacuuming & Mopping Sweeping & Dusting
Sweeping & Dusting Cleaning The Bedrooms
Cleaning The Bedrooms Cleaning The Bathrooms
Cleaning The Bathrooms Cleaning The Toilets
Cleaning The Toilets Cleaning The Kitchen
Cleaning The Kitchen Cleaning The Sinks
Cleaning The Sinks Cleaning The Stovetop
Cleaning The Stovetop Cleaning The Living Spaces
Cleaning The Living Spaces

