The Best House Cleaning In Ipswich

Professional, vetted cleaners

Friendly customer support

Recurring discounts

WHY MAID2MATCH?
More Than Just A Cleaning Service

Easily book & pay online
Appointments are booked online with one simple process, using your phone or computer.

The same cleaner every time
When you book a regular cleaning service with us you'll have the same cleaner for each service.

Cleaning products provided
For your convenience, your cleaner brings their own cleaning equipment for each service.

Easily book and pay online

The same cleaner every time

Cleaning products provided

Adaptable to your needs & preferences

Convenient booking management

No lock-in contracts for ongoing services

Adaptable to your needs & preferences
Our Ipswich cleaners are always flexible and will adapt their services to your cleaning needs.

Convenient booking management
Whatever you need regarding your service, we’re just a message away!

No lock in contracts for ongoing services
You control your cleaning services, with no locked-in long-term contract.

1800 207 686
MAKING YOUR HOME SPARKLE
Flat Rate House Cleaning Service

Book a flat rate service when you need a full house clean. Our Ipswich cleaners will follow our detailed service checklist throughout your home. Extras are available at additional flat rates and a deep clean can be added for homes that haven't been professionally cleaned recently. Hourly cleans available upon request.
MAKING YOUR HOME SPARKLE
House Cleaning Service Options
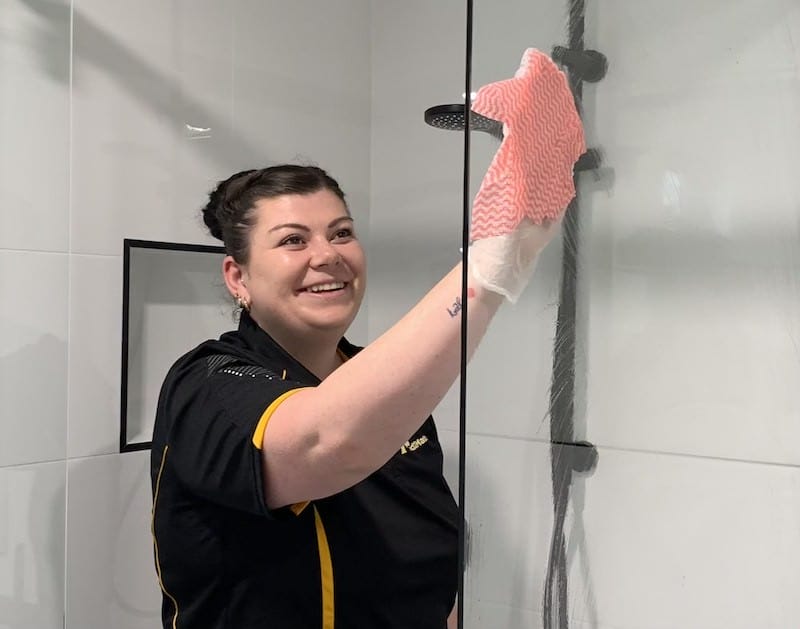


Flat Rate Cleaning
Choose this for: you need a full house clean. This fixed price service means our cleaners will follow our detailed service checklist throughout your home. Extras are available at additional flat rates. A deep clean can be added for homes that haven't been professionally cleaned recently.

What's Included in the Flat Rate?
 Vacuuming & Mopping
Vacuuming & Mopping Sweeping & Dusting
Sweeping & Dusting Cleaning The Bedrooms
Cleaning The Bedrooms Cleaning The Bathrooms
Cleaning The Bathrooms Cleaning The Toilets
Cleaning The Toilets Cleaning The Kitchen
Cleaning The Kitchen Cleaning The Sinks
Cleaning The Sinks Cleaning The Stovetop
Cleaning The Stovetop Cleaning The Living Spaces
Cleaning The Living Spaces


Hourly Rate Cleaning
Choose this for: you need a quick cleaning job, or a tidy-up in specific areas of your home. This time-based service means our cleaners will accommodate your cleaning priorities or focus on what needs cleaning the most. They’ll only work to the allotted time you've booked in for.
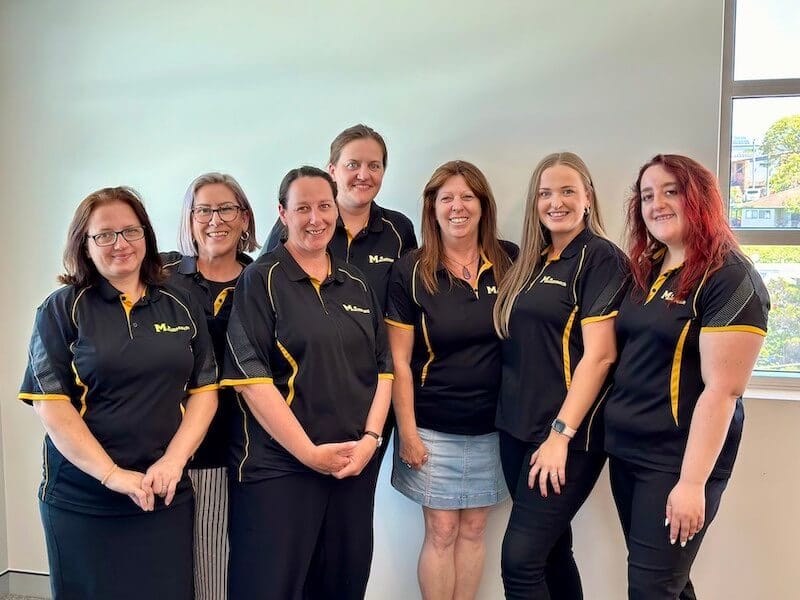

ABOUT MAID2MATCH
Making A Difference In The Cleaning Industry
Our professional cleaners in Ipswich are led by our wonderful Team Leader, Mihaela (pictured on the far left). Mihaela joined Maid2Match in March 2022, bringing decades of cleaning expertise with her. As a result of Mihaela's amazing work ethic and attention to detail, she's received multiple promotions and now manages over 15 Ipswich cleaners.
Maid2Match cleaners have the opportunity to create a career out of their passion for cleaning. We genuinely care about the service we provide and helping our clients by making life a little bit easier.
100% Satisfaction Guarantee
Our professional cleaners take pride in their work, which will be evident when you return home to a sparkling clean house!
After each house clean with Maid2Match, you'll receive an email to rate the service out of 5 stars and leave an optional comment.
If you rate your clean less than 5 stars, we will be in touch to learn more about what can be improved.
All of your feedback is passed on to our employee cleaners, so they can learn what you're happy with and what can be done better at the next service.
While we are confident about our high quality cleaning services, in the rare case you are not satisfied, we will organise a time for your cleaner to return and fix the job.
If you are still not happy after the re-clean, we’ll offer either a partial or full refund on your booking.
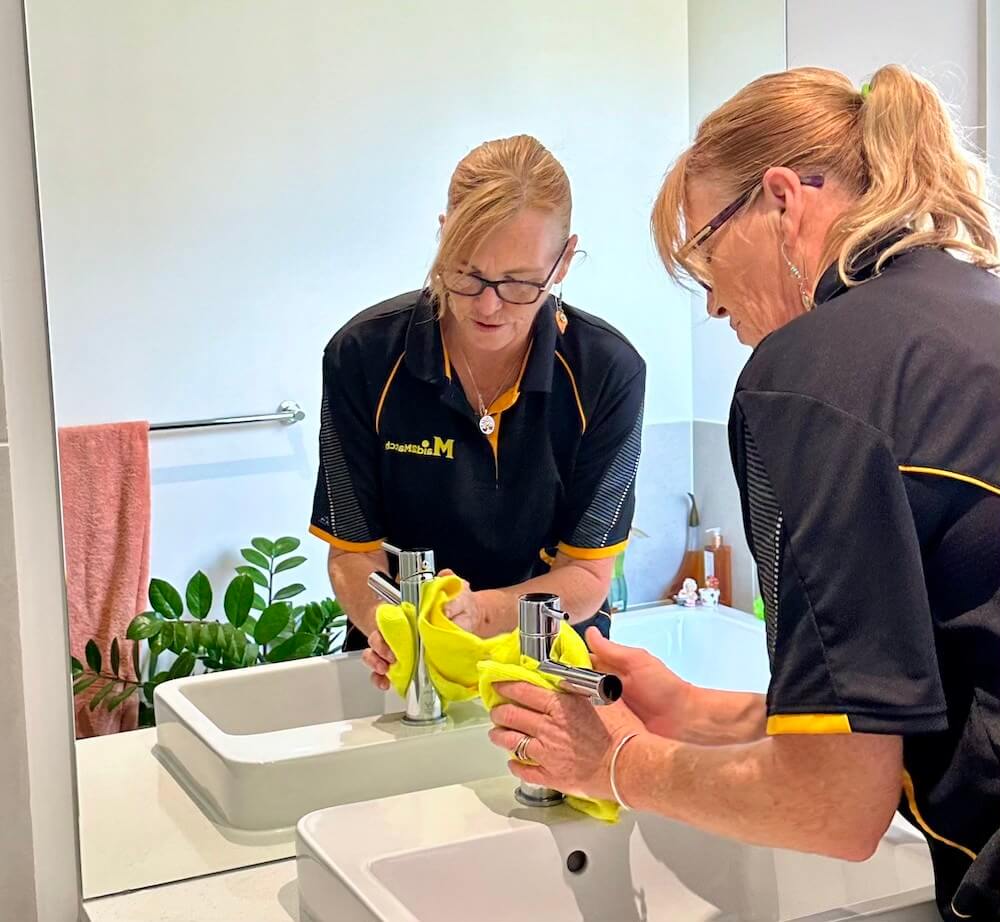

OUR IPSWICH CLEANING TEAM
Meet Some Of Our Maid2Match Cleaners
Elizabeth
Maid2Match Trainer
Mihaela
Maid2Match Field Team Leader

Lia
Maid2Match Trainer
Elizabeth
Maid2Match Trainer
Mihaela
Maid2Match Field Team Leader
Lia
Maid2Match Trainer
Your home is safely insured with us

450+ FIVE STAR REVIEWS ON GOOGLE
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Ipswich Cleaning Information
What time are your services available?
You can arrange for your cleaning job anytime between 8:00am and 5:00pm, Monday to Friday. We allot a 30 minute window for when the cleaning will start, so you know exactly when to expect our cleaner’s arrival. Please note that we do not operate on public holidays.
How much does it cost to clean my house?
For a domestic cleaning service, we have two pricing choices: flat rate and hourly rate. You can find out more about our prices on our pricing page. Pick which service best fits for your cleaning requirements, then use our easy online form for an instant quote!
What services are included?
We offer hourly rate cleaning for specified home areas and quick tidy-ups, or flat rate cleaning for more detailed cleaning jobs and further tasks. Each booking is independent and will depend on your cleaning needs and priorities. You can schedule specific services only, or opt for a deep clean that follows our comprehensive checklist.
Are cleaning supplies provided?
Your Maid2Match cleaner will bring their own (eco-friendly) supplies and gear for your convenience. If you’d prefer we use any particular products, feel free to let us know and we’ll use any supplies you leave out.
Are your cleaning supplies safe for children and pets?
How does a recurring service work?
Do I have to be home for the cleaning service?
Nope, you don't have to be home for our house cleaning services! Just place the key somewhere accessible and our cleaning team will go from there. Please let our customer support team know how the cleaners can access your home. Then rest assured that our team will do a thorough job while seeing to the safety and security of your home.
How long does it take to clean my house?
How easily can I book online?
What forms of payment do you accept?
MAKING YOUR HOME SPARKLE
Ipswich Cleaning Recommendations
What Are the House Cleaning Prices In Ipswich?
The house cleaning prices in Ipswich range from $34 to $65/hr. You can also typically expect flat rate domestic pricing from $70 to $220 for weekly and monthly cleans. Prices for bond cleans are generally from $150 to $800 depending on the size of the home.
Here are some of the current statistics on Ipswich services:
|
Average Cleaning Service Price |
$142.62 |
|
Average Positive Customer Review |
99% |
|
Average Home Size |
3.13 beds and 1.56 baths |
Cleaning Facts
|
Weekly Clean |
24% |
|
Every 2 Weeks |
53% |
|
Every 3 Weeks |
9% |
|
Monthly Cleaning |
14% |
|
House with a Deep Clean |
5% |
|
Clear Interior Windows |
2% |
|
Oven Cleaning |
1% |
|
Housekeeping Extras |
8% |
Jobs In Ipswich In The Last Month
Jobs In The Last Month
Hours Saved
Professional Cleaners


Book A House Cleaning In Ipswich Today
October means it’s jacaranda festival time as the city fills with purple blooms. From Goodna to Evan Marginson Park, Ipswich is all spruced up. And your home needs to be spruced up as well — springtime means spring cleaning!
Go ahead and enjoy the festival, and all the other sights that Ipswich has to offer. Maid2Match will handle the cleaning, no matter the season. Put your home in our capable hands and head out to enjoy yourself — we’ll have everything looking good as new when you get back.

WE DON'T JUST CLEAN HOMES
Other Services We Offer

At the end of your lease? Let Maid2Match clean your home inside and out, with our detailed checklist that covers everything your agent will look for.

Maid2Match is proud to serve customers of all abilities. We accommodate your needs and preferences, and work according to your NDIS Plan to keep your home clean.

From your reception area to your break rooms, we’ll have your workplace sparkling. Book a cleaning service with us and get a spotless office, guaranteed.

From your reception area to your break rooms, we’ll have your workplace sparkling. Book a cleaning service with us and get a spotless office, guaranteed.

At the end of your lease? Let Maid2Match clean your home inside and out, with our detailed checklist that covers everything your agent will look for.

Maid2Match is proud to serve customers of all abilities. We accommodate your needs and preferences, and work according to your NDIS Plan to keep your home clean.

IPSWICH HOUSE CLEANING LOCATIONS
Popular Suburbs
IPSWICH HOUSE CLEANING LOCATIONS
 Vacuuming & Mopping
Vacuuming & Mopping Sweeping & Dusting
Sweeping & Dusting Cleaning The Bedrooms
Cleaning The Bedrooms Cleaning The Bathrooms
Cleaning The Bathrooms Cleaning The Toilets
Cleaning The Toilets Cleaning The Kitchen
Cleaning The Kitchen Cleaning The Sinks
Cleaning The Sinks Cleaning The Stovetop
Cleaning The Stovetop Cleaning The Living Spaces
Cleaning The Living Spaces


